The Importance of Fully Human Antibody Therapeutics
What are Fully Human Antibodies?
- Antibodies from human sources consisting solely of fully human sequences
- No murine sequences, which are commonly used in animal testing
- Produced by using phage display technology to identify the desired human antibody genes, and then introducing the desired sequences into transgenic mice
- Simplifies manufacture of antibody therapeutics due to lower expected immunogenicity compared to animal-derived antibody sequences
| Antibody Development Trends |
1970s
Murine Antibodies

Mouse Antibody Sequences |
1980s
Chimeric Antibodies
Human Antibody Sequences |
1990s
Humanized Antibodies
Human Antibody Sequences |
Reduced Immunogenicity and Side Effects
2000s
Fully Human Antibodies
Human Antibody Sequences |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratios in Global Antibody Therapeutics Development |
1990~1999
2000~2010
|
|||
- Pharmacokinetic properties determining a drug’s safety and efficacy impacted by immunogenicity
- Demonstrated advantage of fully human antibodies or at least humanized antibodies in clinical trials.
Number of Approved Antibody Therapeutics (Cumulative Total)
*Source: Immunotherapy Vol. 11, No. 2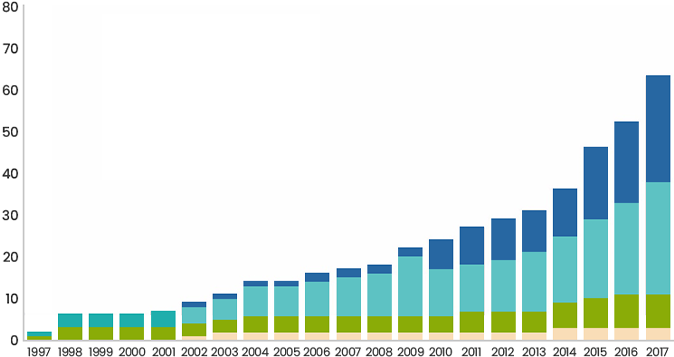
The number of humanized or fully human antibodies among FDA-approved antibody therapeutics has been increasing each year.
- Human
- Humanized
- Chimeric
- Murine
The First Step in Developing a Fully Human Antibody Therapeutic from a Targeting Protein
Phage Display Technology
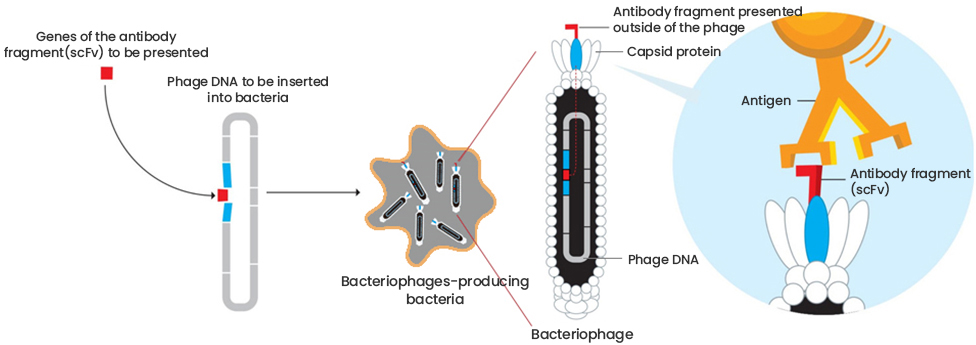
In phage display, genetic information of a target protein is inserted into the genome of a phage so that the target protein is exposed on the surface of the phage, enabling the production of fully human antibodies that are nearly identical to antibodies produced by the human body.
Phages, the smallest type of viruses, mainly infect bacteria. Because of their miniscule size, hundreds of billions can exist in just 1 mL of solution.
After the antibodies are presented on the surface of a phage, the process of selecting an antibody that binds to the target antigen becomes much simpler. Antibody presentation on the surface of the phage can be accomplished by inserting the genes of a human antibody into the phage’s genome through genetic engineering.
All antibody genes produced by a human body can be inserted into phage genes to create a collection of phages displaying the diverse antibodies. This collection of antibody-presenting phages is called a phage display library or human antibody library.
The key to producing a comprehensive human antibody library is to obtain every gene for each antibody produced in the human body and use molecular biology techniques that insert the antibody genes into the phage genes without any loss.
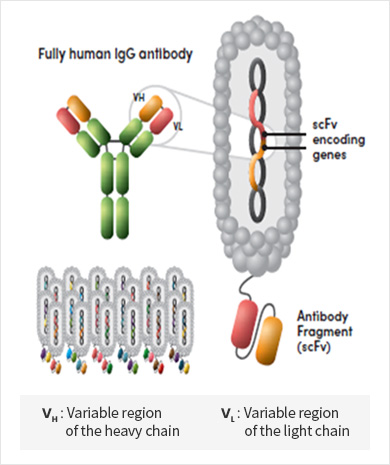
Ymax®-ABL, the Initiation Point of all Novel Therapeutic Antibody R&D at Y-Biologics
-
01
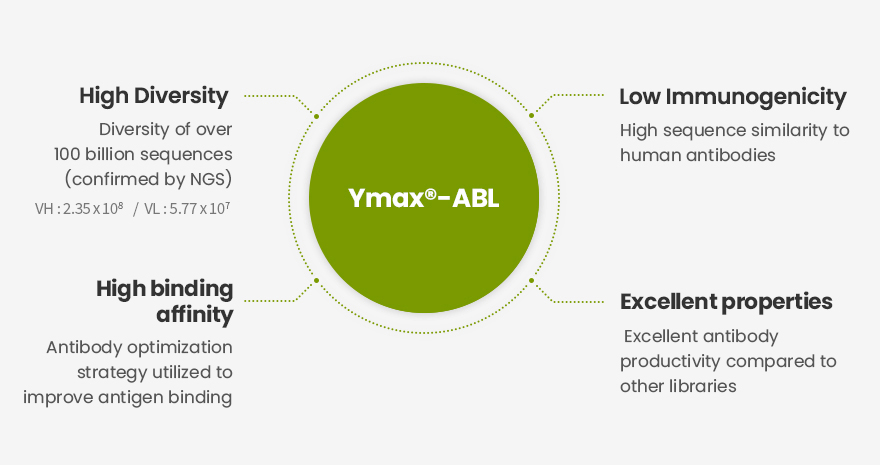
World-class Fully Human Antibody Library
World-class naïve cDNA library of fully human antibodies
More than 100 billion different antibody genes presented through phage display, a technology using genetic recombination to express proteins on the surface of viruses and enabling mass production of antibodies by finding specific enzymes that bind to antibodies
-
02
Launchpad for Each Pipeline Projects
All novel antibodies discovered independently are selected from Ymax®-ABL
-
03
Increased Diversity and Excellent Antigen Binding
Diversity enhanced by using a shuffling strategy during the manufacturing process
Excellent antigen binding
-
04
Clinical Trials for YBL-006 in 3 Countries
YBL-006, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, is a new therapeutic antibody candidate discovered from Ymax®-ABL and developed in-house that is currently undergoing Phase 1 clinical trials in Korea, Australia, and Thailand
-
05
High Sequence Similarity to Human Antibodies
Lower immunogenicity, or the ability of an antigen to trigger an immune response, compared to synthetic libraries
Superior antibody productivity and physical properties compared to synthetic libraries
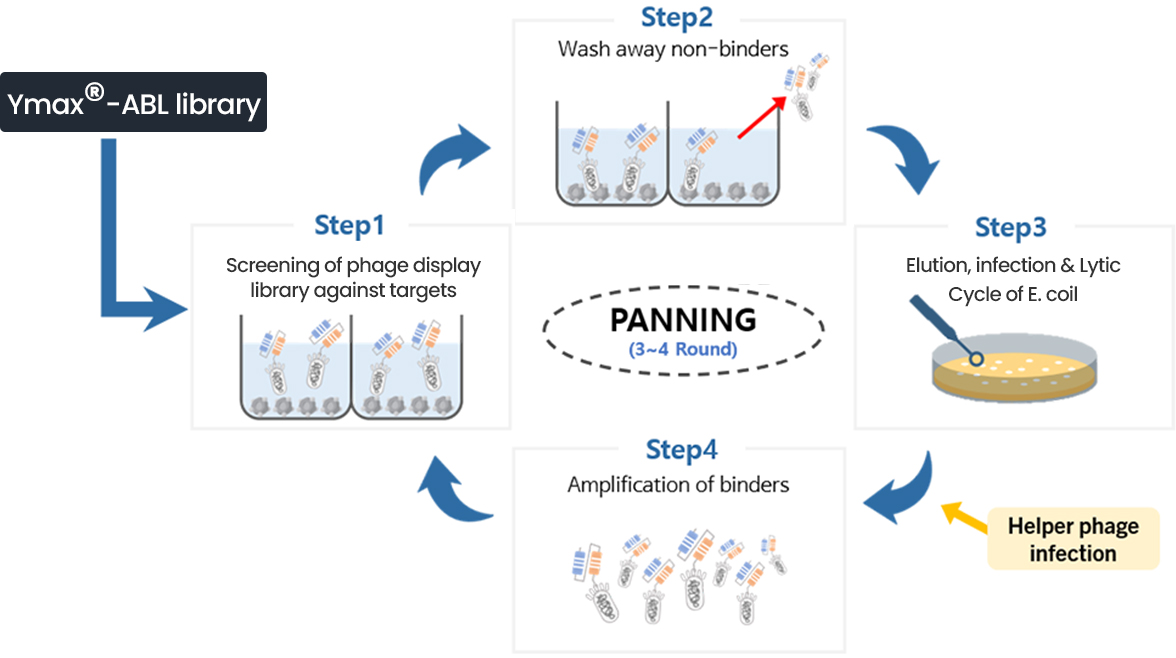
Discovering Suitable Antibodies through Biopanning
Biopanning is the process of selecting an antibody pool that binds to a specific antigen from an antibody library. In our pursuit of discovering top-tier antibodies, this process is just as important as the diversity of our Ymax®-ABL library.
In acknowledgement of its importance, Y-Biologics is optimizing and applying a wide range of biopanning methods. In particular, we are developing and applying novel cell panning technology to antigens for antibodies which are challenging to screen and select.
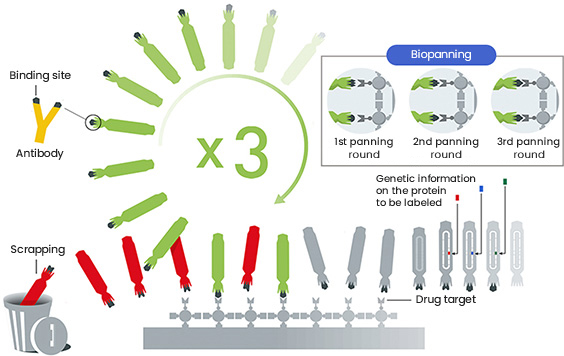
Production of Antibodies with High Potential for Development
An antibody library
with high diversityA phage display system for labeling target proteins
Diverse biopanning methods to find the desired antibodies
An efficient system enabling prompt
analysis of discovered antibodyHigh quality of
antibodies discovered from the library


